Table of Contents
Introduction ................................................................................................... i–iv
What is Engaging Mathematics, Volume I: Grade 8? ............................................ iii
What is found in an Engaging Mathematics TEKS-based activity? .......................... iv
Number and operations ................................................................................ 2–11
Sets of Real Numbers 8(2)(A) ........................................................................... 2
Irrational Numbers 8(2)(B) ............................................................................... 4
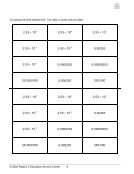
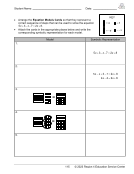
Scientific Notation, Activity 1 8(2)(C) ................................................................. 6
Scientific Notation, Activity 2 8(2)(C) ............................................................... 10
Proportionality ........................................................................................... 12–85
Proportionality and Similar Shapes 8(3)(A) ....................................................... 12
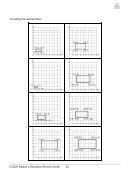
Dilations on a Coordinate Plane, Activity 1 8(3)(B) ............................................ 14
Dilations on a Coordinate Plane, Activity 2 8(3)(B) ............................................ 16
Dilations on a Coordinate Plane, Activity 3 8(3)(C) ............................................ 20
Dilations on a Coordinate Plane, Activity 4 8(3)(C) ............................................ 22
Slope 8(4)(A) ............................................................................................... 26
Rate of Change, Slope, and y-intercept, Activity 1 8(4)(C) ................................. 28
Rate of Change, Slope, and y-intercept, Activity 2 8(4)(C) ................................. 30
Rate of Change, Slope, and y-intercept, Activity 3 8(4)(C) ................................. 32
Rate of Change, Slope, and y-intercept, Activity 4 8(4)(C) ................................. 34
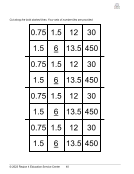
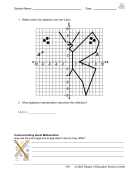
Representations of Proportional Situations, Activity 1 8(5)(A) ............................. 36
Representations of Proportional Situations, Activity 2 8(5)(A) ............................. 38
Representations of Proportional Situations, Activity 3 8(5)(A) ............................. 42
Representations of Non-Proportional Situations, Activity 1 8(5)(B) ...................... 44
Representations of Non-Proportional Situations, Activity 2 8(5)(B) ...................... 48
Trend Lines, Activity 1 8(5)(D) ........................................................................ 50
Trend Lines, Activity 2 8(5)(D) ........................................................................ 52
Direct Variation 8(5)(E) ................................................................................. 54
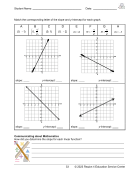
Representations of Linear Relationships, Activity 1 8(5)(F) ................................. 56
Representations of Linear Relationships, Activity 2 8(5)(F) ................................. 58
Representations of Linear Relationships, Activity 3 8(5)(F) ................................. 62
Representations of Linear Relationships, Activity 4 8(5)(F) ................................. 64
Representations of Linear Relationships, Activity 5 8(5)(F) ................................. 68
Functional Relationships, Activity 1 8(5)(G) ...................................................... 72
Functional Relationships, Activity 2 8(5)(G) ...................................................... 74
Proportional and Non-Proportional Relationships, Activity 1 8(5)(H) ..................... 76
Proportional and Non-Proportional Relationships, Activity 2 8(5)(H) ..................... 78
Equations that Model Linear Relationships, Activity 1 8(5)(I) .............................. 80
Equations that Model Linear Relationships, Activity 2 8(5)(I) .............................. 82
Equations that Model Linear Relationships, Activity 3 8(5)(I) .............................. 84
Expressions, equations, and relationships................................................ 86–137
Volume of a Cylinder 8(6)(A) .......................................................................... 86
Modeling the Pythagorean Theorem, Activity 1 8(6)(C) ...................................... 88
Modeling the Pythagorean Theorem, Activity 2 8(6)(C) ...................................... 90
Volume of Cylinders, Activity 1 8(7)(A) ............................................................ 92
Volume of Cylinders, Activity 2 8(7)(A) ............................................................ 94
Volume of Cylinders, Activity 3 8(7)(A) ............................................................ 96
Volume of Cones 8(7)(A)................................................................................ 98
Volume of Spheres 1 8(7)(A) ........................................................................ 100
Surface Area, Activity 1 8(7)(B) .................................................................... 102